Welcome to SfdcIndia
Chatbots vs Copilots vs Agents
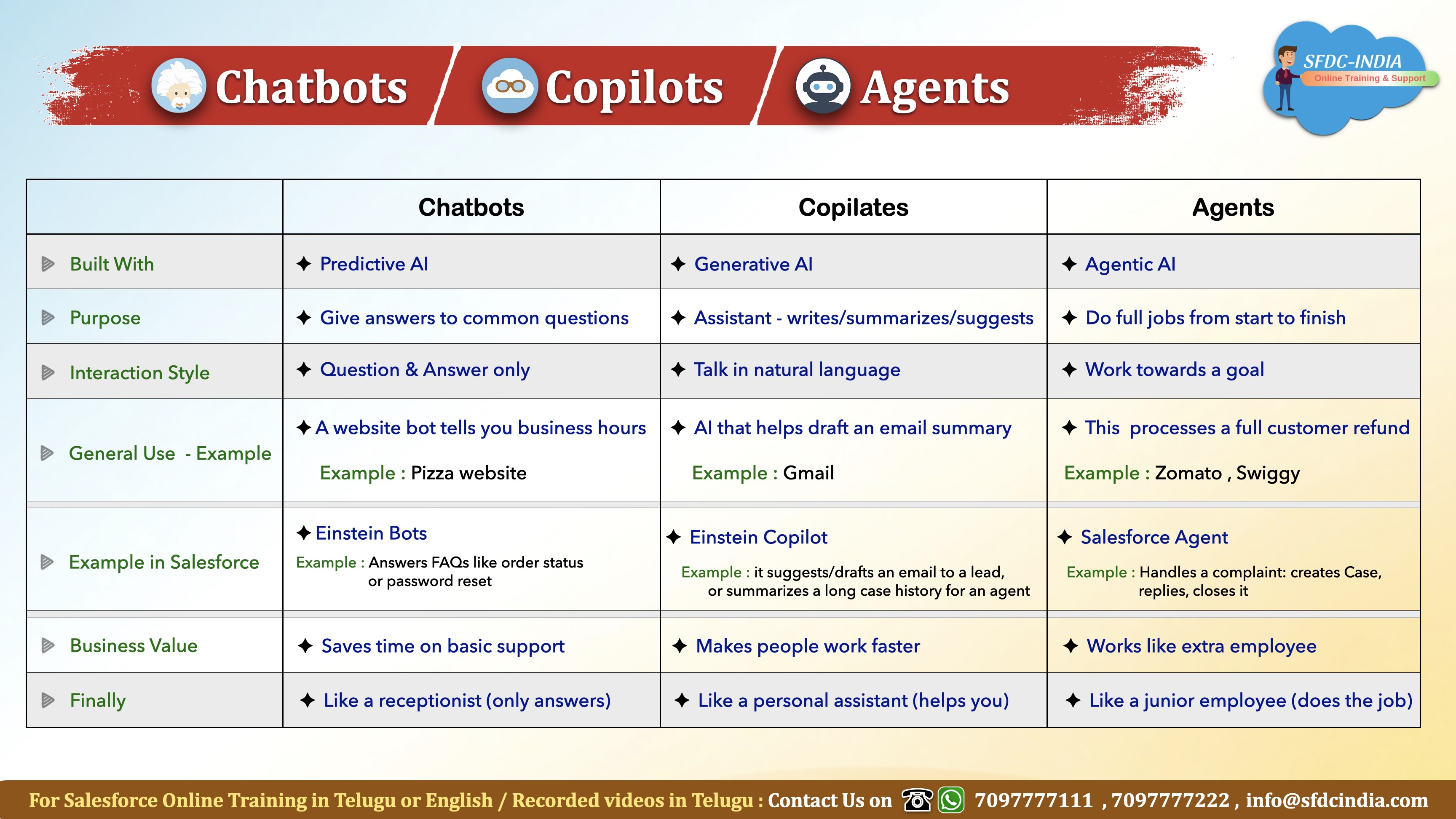
Differences between Chatbots, Copilots, and Agents
Evolution of Salesforce AI Helpers
Chatbots — Answer
- What it is: Q&A helper for common questions (FAQ style).
- Built with: Rules + basic NLP/ML (predictive intent matching).
- How it works: User asks → bot matches keywords/intent → returns a predefined reply or link.
- Strengths: Fast responses, consistent, low cost.
- Limits: Script-based; can’t generate content or handle multi-step tasks.
- When to use: Help center, order status, password reset, simple routing.
- Salesforce Example: Einstein Bots for website/WhatsApp FAQ.
Data Point: Industry studies show 70% of customer service chats can be resolved by bots answering FAQs.
Copilots — Assist
- What it is: Smart assistant that writes, summarizes, or suggests content.
- Built with: Generative AI (LLMs).
- How it works: User asks in natural language → model reads CRM context → drafts email/summary/answer → you review & approve.
- Strengths: Saves time, understands free text, creates good quality drafts.
- Limits: Doesn’t act independently; requires user approval.
- When to use: Drafting emails, summarizing cases, analyzing opportunities.
- Salesforce Example: Einstein Copilot inside CRM.
Data Point: According to Salesforce, Copilot can reduce response drafting time by 40% and boost agent productivity by 27%.
Agents — Act
- What it is: An autonomous digital worker that completes tasks end-to-end.
- Built with: Agentic AI = LLM + tools/automation (Flows/APIs) + governance policies.
- How it works: You set a goal → agent plans steps → calls tools/flows → checks results → repeats until task completes → logs outcome → asks approval at guardrails if needed.
- Strengths: Executes multi-step, cross-app workflows automatically.
- Limits: Needs guardrails, monitoring, and scoped use cases.
- When to use: Case resolution, refunds, data cleanup, customer follow-ups.
- Salesforce Example: AgentForce – creates/updates records, sends replies, closes cases.
Data Point: Salesforce estimates that Agentic AI can automate up to 80% of repetitive service tasks, freeing humans for higher-value work.
